Clean photoinduced generation of free reactive oxygen species by silica films embedded with CdTe–MTA quantum dots
Abstract
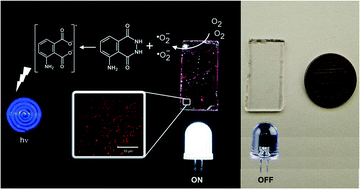
CdTe quantum dots capped with mercaptopropionic acid, 3.5 nm in size, were entrapped in sol–gel films prepared with tetramethyl orthosilicate under mineral acidic catalysis in the presence of Triton X-100 as a non-ionic surfactant. The follow-up of the sol–gel process was performed in real-time both with fluorescent crystal violet as a molecular rotor and with quantum dots. Clusters of nanoparticles 500 nm in size become homogeneously distributed in the films, but preserving initial photoluminescence quantum yields (21%), and the emission spectrum had increased excited state lifetimes (65 ± 4 ns) and photostability. Films photoactivation inside a multi-pumping flow system enabled reproducible generation of reactive oxygen species as determined by chemiluminescence using the alkaline luminol reagent, thus opening future developments for clean and environmentally friendly analytical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...