Tunable dynamic hydrophobic attachment of guest molecules in amphiphilic core–shell polymers†
Abstract
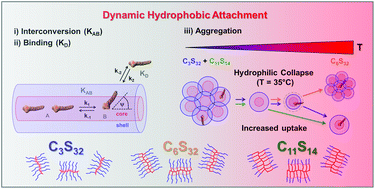
In this study, synthesis and dynamic properties of amphiphilic core–shell polymers are reported as monitored through their interaction with small amphiphilic molecules. Brush-like structures are formed with a hydrophobic core surrounded by a hydrophilic shell utilizing controlled radical addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization of macromonomers consisting of linear polyglycerol chains attached to alkylene methacrylate. Continuous wave electron paramagnetic resonance (CW EPR) spectroscopy is employed to study how the amphiphilic, paramagnetic spin probe 16-DSA (16-doxyl stearic acid) interacts with polymers of different alkylene chain lengths in their hydrophobic cores and different polyglycerol chain lengths in their hydrophilic shells. The spin probe exhibits dynamic hydrophobic attachment to the polymers and reveals an indirect, dynamics-based view of polymer effects such as temperature response, aggregation and ligand binding properties. Increasing the hydrophobic alkylene chain length in the polymers alters the physical properties of the core region significantly. A large set of controllable functional polymer properties can be adjusted by the degree of polymerization and alkylene spacer length. Partial aggregation of the polymers further modifies the binding properties. Applying dynamic light scattering (DLS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and molecular dynamic (MD) simulations, the complex dynamic behavior found with EPR spectroscopy was further complemented and verified.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...