Enhancing the therapeutic effects of polyphenols with macromolecules
Abstract
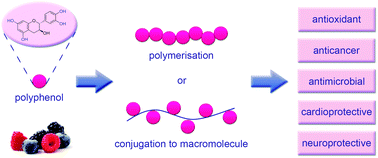
Well-known for their antioxidant properties, polyphenols are naturally occurring compounds containing one or more phenol groups. A high dietary intake of polyphenols has been linked to a reduced incidence of a number of diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis and neurodegenerative diseases. Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo studies show the potential for polyphenols as therapeutic agents with cardioprotective, antimicrobial, anticancer, neuroprotective, and antidiabetic effects demonstrated. Despite their impressive therapeutic effects, polyphenols suffer from a number of drawbacks, including instability when exposed to light, heat and basic conditions; poor bioavailability; rapid metabolism; and poor membrane permeability. These drawbacks limit the clinical applications of polyphenols. Polymers and other macromolecules are well-known for their ability to stabilise and improve the bioavailability of therapeutic agents. A number of macromolecular systems have been developed that stabilise polyphenols whilst enhancing their therapeutic effects, including direct polymerisation of polyphenol monomers via step-growth, free radical and enzyme catalysed reactions; and conjugation with macromolecules via enzyme grafting, free-radical grafting, esterification and amidation. In this review, we will detail the key techniques employed to stabilise polyphenols with macromolecules and provide examples of each technique.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...