Downsizing the BAD BH3 peptide to small constrained α-helices with improved ligand efficiency†
Abstract
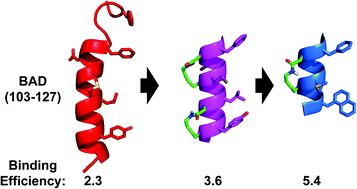
Bcl2 Homology (BH) proteins can either trigger or prevent programmed cell death or apoptosis. Deregulation of the BH protein family network leads to evasion of apoptosis, uncontrolled proliferation and is a hallmark of cancer. Inhibition of pro-survival BH proteins is a promising chemotherapeutic strategy for certain cancers. We have examined whether helix-constrained peptides based on the BAD BH3 domain (residues 103–127) can be downsized to much smaller more drug-like peptides. We report the preparation, structural characterisation, in vitro Bcl-xL inhibition and leukemic T-cell killing ability of 45 linear, mono-, bi- and tricyclic helical peptidomimetics between 8- and 19-residues in length. We show that the BAD BH3 can be downsized to 8–14 residues and still maintain appreciable affinity for Bcl-xL. In addition, the binding efficiency indices (BEI) of the downsized mimetics are significantly higher than the BAD BH3 and similar stapled BH3 mimetics, approaching drug-like molecules. This suggests that bicyclic and monocyclic mimetics based on BH3 domains are much more efficient binding ligands than the longer peptides which they mimic.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Macrocycles with bio-related applications


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...