Radiation damage to single stranded oligonucleotide trimers labelled with 5-iodopyrimidines†
Abstract
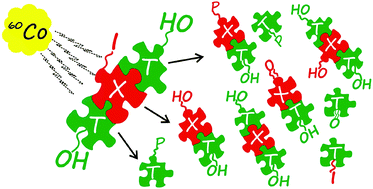
The radiolysis of deoxygenated aqueous solution containing trimeric oligonucleotides labelled with iodinated pyrimidines and Tris-HCl as the hydroxyl radical scavenger leads to electron attachment to the halogenated bases that mainly results in single strand breaks. The iodinated trimers are 2-fold more sensitive to solvated electrons than the brominated oligonucleotides, which is explained by the barrier-free dissociation of the iodinated base anions. The present study fills the literature gap concerning the chemistry triggered by ionizing radiation in the iodinated pyrimidines incorporated into DNA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...