Design and synthesis of unsymmetric macrocyclic hexaoxazole compounds with an ability to induce distinct G-quadruplex topologies in telomeric DNA†
Abstract
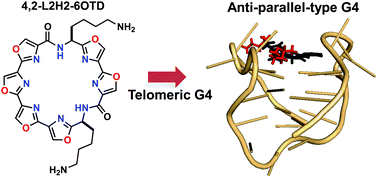
New macrocyclic hexaoxazole compounds bearing two side chains on an unsymmetrical macrocyclic ring system, i.e., 4,2-L2H2-6OTD (2) and 5,1-L2H2-6OTD (3), were designed as candidate G-quadruplex (G4) ligands and synthesized. These G4 ligands 2 and 3 induced an anti-parallel topology and a hybrid-type topology of telomeric DNA, respectively, in contrast to the previously reported symmetrical macrocycle 3,3-L2H2-6OTD (1), which induces a typical anti-parallel structure. Molecular mechanics calculations and docking studies indicate that these differences arise from the different directions of the side chains in these L2H2-6OTD derivatives, and provide an explanation for the weaker stabilization of telomeric DNA by 2 and 3, compared with 1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...