Three-dimensional (3D) plasmonic hot spots for label-free sensing and effective photothermal killing of multiple drug resistant superbugs
Abstract
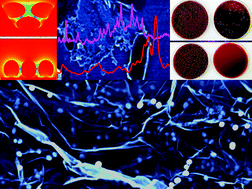
Drug resistant superbug infection is one of the foremost threats to human health. Plasmonic nanoparticles can be used for ultrasensitive bio-imaging and photothermal killing by amplification of electromagnetic fields at nanoscale “hot spots”. One of the main challenges to plasmonic imaging and photothermal killing is design of a plasmonic substrate with a large number of “hot spots”. Driven by this need, this article reports design of a three-dimensional (3D) plasmonic “hot spot”-based substrate using gold nanoparticle attached hybrid graphene oxide (GO), free from the traditional 2D limitations. Experimental results show that the 3D substrate has capability for highly sensitive label-free sensing and generates high photothermal heat. Reported data using p-aminothiophenol conjugated 3D substrate show that the surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) enhancement factor for the 3D “hot spot”-based substrate is more than two orders of magnitude greater than that for the two-dimensional (2D) substrate and five orders of magnitude greater than that for the zero-dimensional (0D) p-aminothiophenol conjugated gold nanoparticle. 3D-Finite-Difference Time-Domain (3D-FDTD) simulation calculations indicate that the SERS enhancement factor can be greater than 104 because of the bent assembly structure in the 3D substrate. Results demonstrate that the 3D-substrate-based SERS can be used for fingerprint identification of several multi-drug resistant superbugs with detection limits of 5 colony forming units per mL. Experimental data show that 785 nm near infrared (NIR) light generates around two times more photothermal heat for the 3D substrate with respect to the 2D substrate, and allows rapid and effective killing of 100% of the multi-drug resistant superbugs within 5 minutes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...