Optofluidic sensing from inkjet-printed droplets: the enormous enhancement by evaporation-induced spontaneous flow on photonic crystal biosilica†
Abstract
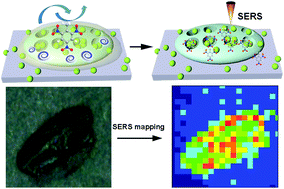
Novel transducers for detecting an ultra-small volume of an analyte solution play pivotal roles in many applications such as chemical analysis, environmental protection and biomedical diagnosis. Recent advances in optofluidics offer tremendous opportunities for analyzing miniature amounts of samples with high detection sensitivity. In this work, we demonstrate enormous enhancement factors (106–107) of the detection limit for optofluidic analysis from inkjet-printed droplets by evaporation-induced spontaneous flow on photonic crystal biosilica when compared with conventional surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensing using the pipette dispensing technology. Our computational fluid dynamics simulation has shown a strong recirculation flow inside the 100 picoliter droplet during the evaporation process due to the thermal Marangoni effect. The combination of the evaporation-induced spontaneous flow in micron-sized droplets and the highly hydrophilic photonic crystal biosilica is capable of providing a strong convection flow to combat the reverse diffusion force, resulting in a higher concentration of the analyte molecules at the diatom surface. In the meanwhile, high density hot-spots provided by the strongly coupled plasmonic nanoparticles with photonic crystal biosilica under a 1.5 μm laser spot are verified by finite-difference time domain simulation, which is crucial for SERS sensing. Using a drop-on-demand inkjet device to dispense multiple 100 picoliter analyte droplets with pinpoint accuracy, we achieved the single molecule detection of Rhodamine 6G and label-free sensing of 4.5 × 10−17 g trinitrotoluene from only 200 nanoliter solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...