Molybdenum carbide nanotubes: a novel multifunctional material for label-free electrochemical immunosensing†
Abstract
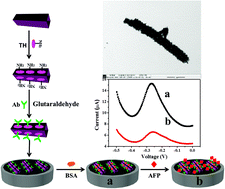
Herein, a multifunctional nanoarchitecture has been developed by integrating well-crystalline molybdenum carbide (Mo2C) nanotubes and an electrochemical indicator – thionin (TH). The Mo2C nanotubes were synthesized through the self-degradable template method and high-temperature calcination, and their structure and morphology were characterized through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Due to the high electrocatalytic properties, excellent conductivity and highly active surface area of Mo2C nanotubes, the Mo2C-based material was used as a nanocarrier to load TH molecules for the development of a label-free electrochemical immunosensor for α-fetoprotein (AFP) detection. The decorated TH probe on the Mo2C nanotubes not only acted as a bridging molecule to effectively capture and immobilize primary anti-AFP on the Mo2C nanotubes, but also acted as a signal indicator for the detection of AFP. The proposed immunosensor exhibited excellent selectivity (with a detection limit of 3 pg mL−1), high stability and good reproducibility by combining the unique structure and features of the Mo2C nanotubes. Furthermore, this sensing platform was finally used for the detection of AFP in human serum with satisfactory results. Therefore, the Mo2C nanotubes can be considered as a candidate carbon material for fabrication of simple, label-free and ultrasensitive electrochemical sensors, broadening the application of this material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...