Functionalized graphene oxide serves as a novel vaccine nano-adjuvant for robust stimulation of cellular immunity†
Abstract
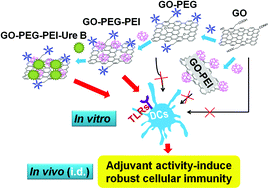
Benefiting from their unique physicochemical properties, graphene derivatives have attracted great attention in biomedicine. In this study, we carefully engineered graphene oxide (GO) as a vaccine adjuvant for immunotherapy using urease B (Ure B) as the model antigen. Ure B is a specific antigen for Helicobacter pylori, which is a class I carcinogen for gastric cancer. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and various types of polyethylenimine (PEI) were used as coating polymers. Compared with single-polymer modified GOs (GO–PEG and GO–PEI), certain dual-polymer modified GOs (GO–PEG–PEI) can act as a positive modulator to promote the maturation of dendritic cells (DCs) and enhance their cytokine secretion through the activation of multiple toll-like receptor (TLR) pathways while showing low toxicity. Moreover, this GO–PEG–PEI can serve as an antigen carrier to effectively shuttle antigens into DCs. These two advantages enable GO–PEG–PEI to serve as a novel vaccine adjuvant. In the subsequent in vivo experiments, compared with free Ure B and clinically used aluminum-adjuvant-based vaccine (Alum-Ure B), GO–PEG–PEI–Ure B induces stronger cellular immunity via intradermal administration, suggesting promising applications in cancer immunotherapy. Our work not only presents a novel, highly effective GO-based vaccine nano-adjuvant, but also highlights the critical roles of surface chemistry for the rational design of nano-adjuvants.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2016 Nanoscale HOT Article Collection

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...