Plasmonic gratings with nano-protrusions made by glancing angle deposition for single-molecule super-resolution imaging†
Abstract
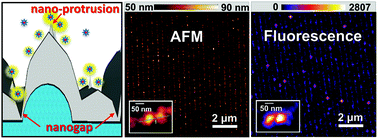
Super-resolution imaging has been advantageous in studying biological and chemical systems, but the required equipment and platforms are expensive and unable to observe single-molecules at the high (μM) fluorophore concentrations required to study protein interaction and enzymatic activity. Here, a plasmonic platform was designed that utilized an inexpensively fabricated plasmonic grating in combination with a scalable glancing angle deposition (GLAD) technique using physical vapor deposition. The GLAD creates an abundance of plasmonic nano-protrusion probes that combine the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) from the periodic gratings with the localized SPR of these nano-protrusions. The resulting platform enables simultaneous imaging of a large area without point-by-point scanning or bulk averaging for the detection of single Cyanine-5 molecules in dye concentrations ranging from 50 pM to 10 μM using epifluorescence microscopy. Combining the near-field plasmonic nano-protrusion probes and super-resolution technique using localization microscopy, we demonstrate the ability to resolve grain sizes down to 65 nm. This plasmonic GLAD grating is a cost-effective super-resolution imaging substrate with potential applications in high-speed biomedical imaging over a wide range of fluorescent concentrations.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...