Detection of early primary colorectal cancer with upconversion luminescent NP-based molecular probes†
Abstract
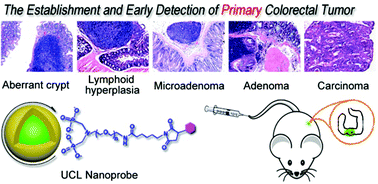
Early detection and diagnosis of cancers is extremely beneficial for improving the survival rate of cancer patients and molecular imaging techniques are believed to be relevant for offering clinical solutions. Towards early cancer detection, we developed a primary animal colorectal cancer model and constructed a tumor-specific imaging probe by using biocompatible NaGdF4:Yb,Er@NaGdF4 upconversion luminescent NPs for establishing a sensitive early tumor imaging method. The primary animal tumor model, which can better mimic the human colorectal cancer, was built upon continual administration of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine in Kunming mice and the tumor development was carefully monitored through histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses to reveal the pathophysiological processes and molecular features of the cancer microenvironment. The upconversion imaging probe was constructed through covalent coupling of PEGylated core–shell NPs with folic acid whose receptor is highly expressed in the primary tumors. Upon 980 nm laser excitation, the primary colorectal tumors in the complex abdominal environment were sensitively imaged owing to the ultralow background of the upconversion luminescence and the high tumor-targeting specificity of the nanoprobe. We believe that the current studies provide a highly effective and potential approach for early colorectal cancer diagnosis and tumor surgical navigation.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanoscale approaches for cancer diagnosis and treatment

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...