Tumor cell-specific photothermal killing by SELEX-derived DNA aptamer-targeted gold nanorods†
Abstract
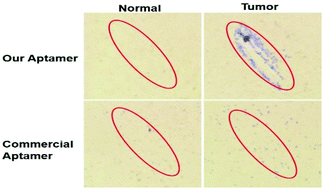
Despite widespread availability of cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents, the killing of tumour cells without affecting healthy surrounding tissue remains elusive, although recent developments in terms of plasmonic nanoparticles capable of photothermal killing have some promise. Here we describe novel DNA aptamer-tethered gold nanorods (GNRs) that act as efficient photothermal therapeutics against tumour cells, but not their isogenic normal cell counterparts. A modified Cell-SELEX process was developed to select a novel DNA aptamer (KW16-13) that specifically recognised and was internalised by cells of the MCF10CA1h human breast ductal carcinoma line but not by those of its isogenic normal counterpart (MCF10A). GNRs conjugated to KW16-13 were readily internalized by the MCF10CA1h tumour cells with minimal uptake by MCF10A normal cells. Upon near infrared (NIR) light irradiation, tumour cell death of >96%, could be effected, compared to <1% in the normal cells or cells incubated with GNRs alone, our KW16-13 aptamer-targeted GNRs thus showing >71-fold tumor cell death than GNRs-targeted with a previously described aptamer. This demonstrates the significant potential for aptamer functionalised-GNRs to be used effective and above all selective anti-cancer photothermal therapeutics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...