Biointeractions of ultrasmall glutathione-coated gold nanoparticles: effect of small size variations†
Abstract
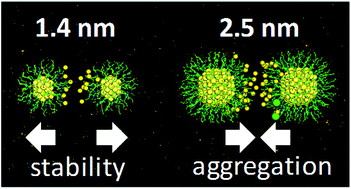
Recent in vivo studies have established ultrasmall (<3 nm) gold nanoparticles coated with glutathione (AuGSH) as a promising platform for applications in nanomedicine. However, systematic in vitro investigations to gain a more fundamental understanding of the particles’ biointeractions are still lacking. Herein we examined the behavior of ultrasmall AuGSH in vitro, focusing on their ability to resist aggregation and adsorption from serum proteins. Despite having net negative charge, AuGSH particles were colloidally stable in biological media and able to resist binding from serum proteins, in agreement with the favorable bioresponses reported for AuGSH in vivo. However, our results revealed disparate behaviors depending on nanoparticle size: particles between 2 and 3 nm in core diameter were found to readily aggregate in biological media, whereas those strictly under 2 nm were exceptionally stable. Molecular dynamics simulations provided microscopic insight into interparticle interactions leading to aggregation and their sensitivity to the solution composition and particle size. These results have important implications, in that seemingly small variations in size can impact the biointeractions of ultrasmall AuGSH, and potentially of other ultrasmall nanoparticles as well.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...