Design and synthesis of new s-triazine polymers and their application as nanoparticulate drug delivery systems†
Abstract
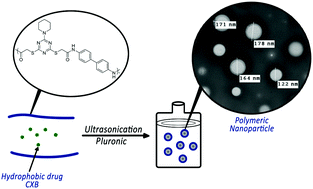
Herein, we report the synthesis of a library of new s-triazine polyamides containing glycine and thioglycolic acid. The reaction of s-triazine dicarboxylic acid derivatives with ethylenediamine, benzidine, piperazine, or p-phenylenediamine, afforded the target designed s-triazine polyamides. The thermal properties of the polymers were evaluated by different techniques, and the thermodynamic parameters of the decomposition processes were evaluated. The feasibility of the synthesized polymers as drug nanodelivery systems was investigated. The nanoparticles were loaded with celecoxib (CXB), an anti-inflammatory drug with a highly promising anti-cancer effect, resulting in high entrapment efficiency levels (62.3–99.8%) with good drug loading in the range 1.58–4.19%. After 48 h, 46.90, 64.20, 57.81, 53.95, and 49.43% of CXB was released from polymeric NPs 26, 43, 44, 45, and 46, respectively, demonstrating a sustained drug release profile. Notably, free CXB, and CXB-loaded polymeric NPs CXB-43, CXB-45, and CXB-46 demonstrated considerable reduction in cell viability in a dose-dependent manner.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...