Novel yttrium and zirconium catalysts featuring reduced Ar-BIANH2 ligands for olefin hydroamination (Ar-BIANH2 = bis-arylaminoacenaphthylene)†
Abstract
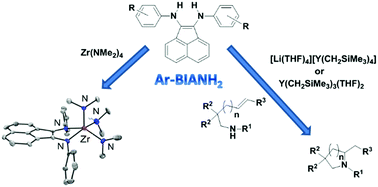
The novel class of bis-arylaminoacenaphthylenes (Ar-BIANH2) was employed for the preparation of zirconium and yttrium complexes to be used as catalysts for cyclohydroamination of a number of primary and secondary aminoalkenes. The complex [(2,6-iPr2C6H3-BIAN)Zr(NMe2)2(η1-NHMe2)] was isolated and completely characterized, including X-ray diffraction analysis. Despite its easy and almost quantitative isolation, it showed only moderate catalytic performance in the intramolecular hydroamination, irrespective of the cyclization precursor used. On the other hand, in situ generated YIII complexes obtained using the same class of ligands were found to be very active, leading to the hydroamination of substrates including those normally reluctant in undergoing cyclization such as those featuring an internal non-activated C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond. Electron donating substituents and especially steric hindrance on the ligand improve the performance of the catalysts, allowing us to decrease the catalyst loading to 1 mol% in the latter case.
C double bond. Electron donating substituents and especially steric hindrance on the ligand improve the performance of the catalysts, allowing us to decrease the catalyst loading to 1 mol% in the latter case.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...