Hierarchically porous monolithic silica with varying porosity using bis(trimethoxysilyl)arenes as precursors†
Abstract
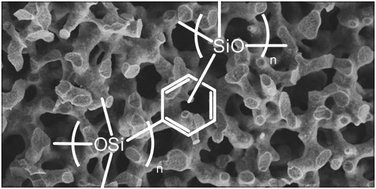
The ortho-, meta- and para-isomers of bis(trimethoxysilyl)benzene and bis((trimethoxysilyl)phenyl)dimethoxysilane were synthesized from their corresponding diarylbromides. Mixtures of these bis(trimethoxysilyl)arenes and tetramethoxysilane (TMOS) were used as organosilica precursors for the preparation of macro-mesoporous silica monoliths using different amounts of the porogen poly(ethylene glycol) to investigate the effect on the porosity of the final materials. The prepared samples were characterized by nitrogen and dibromomethane sorption measurements, mercury intrusion porosimetry and scanning electron microscopy. The analysis of dibromomethane isotherms indicated a significantly lower polarity of the mesopore surface compared to that of pure SiO2 monoliths, proving the presence of arene units at the mesopore surfaces.
- This article is part of the themed collection: The Creative World of Porous Materials

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...