Accessible bidentate diol functionality within highly ordered composite periodic mesoporous organosilicas†
Abstract
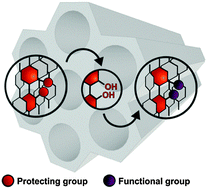
Periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) materials containing methoxy- or methoxyethoxymethyl-ether protected biphenol dopants were synthesized and the protecting groups were cleaved to liberate reactive C2-symmetric diols within the solid-state material. Treatment of the deprotected PMO materials with phosphoryl chloride yielded phosphate ester functional groups predominantly at the exposed biphenol sites, while protected materials showed only surface phosphate species. Since biphenols are closely related to common ligands for asymmetric catalysis, these results open up significant possibilities for the design of chiral recoverable catalysts with chiral groups embedded in the walls of the material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...