Charge transfer complexes of 4-isopropyl-2-benzyl-1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one1,1-dioxide with DDQ and TCNE: experimental and DFT studies
Abstract
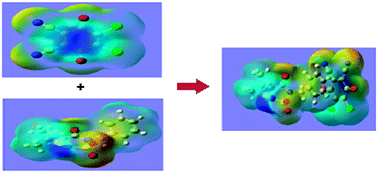
The charge transfer complexes of the donor 4-isopropyl-2-benzyl-1,2,5-thiadiazolidin-3-one1,1-dioxide (SF) with π acceptors 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ) and tetracyanoethylene (TCNE) have been studied spectrophotometrically in chloroform and methanol at room temperature. The results indicated the formation of CT-complexes with a molar ratio of 1 : 1 between donor and each acceptor. The physical parameters of the CT-complexes were evaluated using the Benesi–Hildebrand equation. The data were analyzed in terms of their stability constant (K), molar extinction coefficient (εCT), thermodynamic standard reaction quantities (ΔG0, ΔH0, ΔS0), oscillator strength (f), transition dipole moment (μEN) and ionization potential (ID). The experimental studies were complemented by quantum chemical calculations by the time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) at the B3LYP level. The theoretical UV visible and FT-IR spectra were compared with those obtained experimentally. The first order hyperpolarizability (β0) and related properties (α0 and Δα) are calculated using the B3LYP method on the finite-field approach. The Mulliken charges, MEP calculations, the electronic properties, HOMO and LUMO energies and NBO analysis were performed on an optimized charge transfer complex of SF-DDQ.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...