Formation of hybrid core–shell microgels induced by autonomous unidirectional migration of nanoparticles†
Abstract
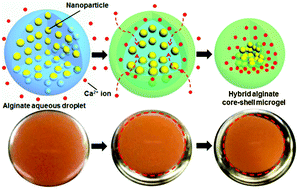
This Communication describes a facile strategy for the fabrication of inorganic nanoparticle (NP)-loaded hybrid core–shell microgels. The formation of core–shell microgels constitutes a novel mechanism in which the ionic-crosslinking of charged polymers (e.g., alginate) drives the unidirectional migration of NPs towards the centre of droplets. This versatile strategy allows the encapsulation of inorganic NPs with different sizes, shapes and surface properties in the core of the microgels in a single step.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...