Natural products and their derivatives as tRNA synthetase inhibitors and antimicrobial agents†
Abstract
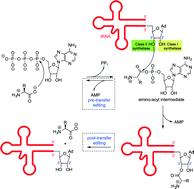
The tRNA synthetase enzymes are promising targets for development of therapeutic agents against infections by parasitic protozoans (e.g. malaria), fungi and yeast, as well as bacteria resistant to current antibiotics. These ubiquitous enzymes load a particular amino acid onto its cognate tRNA to form an aminoacyl tRNA in preparation for protein synthesis by the ribosome. Although tRNA synthetases for a given amino acid are often similar in different organisms, slight differences in their sequence and structure can permit highly selective interaction with inhibitors. Hence, these enzymes have been successful targets of anti-infective agents for decades. They can also act as anticancer agents by preventing protein synthesis in human cells. Many inhibitors have been isolated from nature or have designs inspired by natural products. This review lists known naturally derived aaRS inhibitors and particularly aims to highlight advances in our understanding of their application as antibacterial, anticancer and antimalarial therapeutics. Advances in structural understanding, overcoming resistance and increasing inhibitor efficacy will also be discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...