Recent advances in the rational design and optimization of antibacterial agents†
Abstract
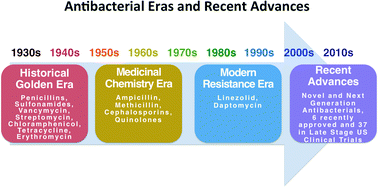
This review discusses next-generation antibacterial agents developed using rational, or targeted, drug design strategies. The focus of this review is on small-molecule compounds that have been designed to bypass developing bacterial resistance, improve the antibacterial spectrum of activity, and/or to optimize other properties, including physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. Agents are discussed that affect known antibacterial targets, such as the bacterial ribosome, nucleic acid binding proteins, and proteins involved in cell-wall biosynthesis; as well as some affecting novel bacterial targets which do not have currently marketed agents. The discussion of the agents focuses on the rational design strategies employed and the synthetic medicinal chemistry and structure-based design techniques utilized by the scientists involved in the discoveries, including such methods as ligand- and structure-based strategies, structure–activity relationship (SAR) expansion strategies, and novel synthetic organic chemistry methods. As such, the discussion is limited to small-molecule therapeutics that have confirmed macromolecular targets and encompasses only a fraction of all antibacterial agents recently approved or in late-stage clinical trials. The antibacterial agents selected have been recently approved for use on the U.S. or European markets or have shown promising results in phase 2 or phase 3 U.S. clinical trials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...