Radiolabeled analogs of neurotensin (8–13) containing multiple 1,2,3-triazoles as stable amide bond mimics in the backbone†‡
Abstract
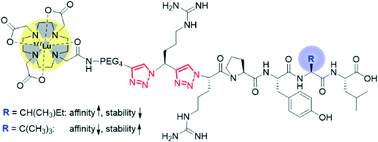
Radiometallated regulatory peptides are a promising class of radiopharmaceuticals for the diagnosis (imaging) and therapy of cancer in nuclear oncology. A limitation of such peptides employed as tumor-specific vectors is represented by their low stability in vivo. Stabilization of the peptides against proteolytic degradation by, e.g., structural modifications, can improve their tumor-targeting properties. We here report an application of our recently introduced peptide stabilization methodology, which involves the substitution of amide bonds in the backbone of peptides by metabolically stable 1,2,3-triazoles. Specifically, we replaced multiple amide bonds by the heterocyclic amide bond mimic in the binding sequence of neurotensin, NT(8–13), and studied in vitro the effect of the modifications on the biological properties of the peptidomimetics obtained (cell internalization, affinity towards the neurotensin receptor subtype 1, blood plasma stability, and log D). In the course of the work, a 177Lu-labeled DOTA-NT(8–13) conjugate bearing two consecutively placed triazoles in its backbone with retained biological function was identified.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...