The discovery and evaluation of diaryl ether heterocyclic sulfonamides as URAT1 inhibitors for the treatment of gout†‡
Abstract
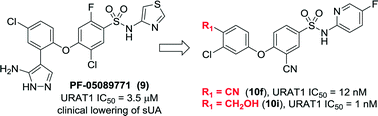
Elevated serum uric acid levels can lead to gout which remains an area of unmet medical need. Following an unexpected clinical uricosuric effect observed with a sulfonamide compound, PF-05089771 (9), subsequently attributed to weak URAT1 inhibition, the optimization of a series of acidic sulfonamides as selective URAT1 inhibitors was undertaken. Compounds 10f and 10i were identified as suitable leads for more extensive profiling after exhibiting high URAT1 inhibitory potency and subsequently demonstrated promising preclinical ADME and safety profiles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...