Abstract
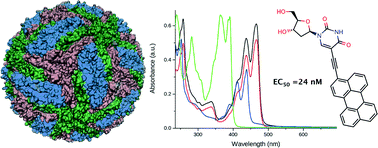
Rigid amphipathic fusion inhibitors (RAFIs), 5-arylethynyl uracil nucleosides with bulky aryl groups, appeared to have considerable activity against tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) in cell culture. The rigid ethynyl linker and perylene residue are essential structural prerequisites for high activity, giving EC50 values of 18 and 24 nM for 5-(perylen-3-yl)ethynyl-arabino-uridine and 5-(perylen-3-yl)ethynyl-2′-deoxy-uridine, respectively, upon simultaneous mixing of the compounds, cells and virus.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...