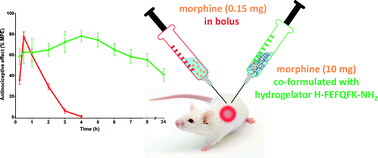
Abstract
Herein, a family of hydrogel-forming peptides was designed starting from the short, tunable and amphipathic hexapeptide hydrogelator H-Phe-Glu-Phe-Gln-Phe-Lys-OH (1). The hydrophobic side chains as well as the nature of both N- and C-termini were modified in order to obtain suitable gelation conditions and drug release profiles for in vivo application. To potentially increase the enzymatic stability, an all-D analogue was prepared as well. After their macroscopic and microscopic characterization by rheology and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis, opioid drugs were encapsulated into the hydrogels and sustained release experiments were carried out. Hydrogel toxicity was assessed in cell viability assays. Based on the physicochemical, mechanical, and noncytotoxic properties, H-Phe-Glu-Phe-Gln-Phe-Lys-NH2 (2) was further investigated for in vivo release of morphine. The antinociceptive effects following subcutaneous injection of the morphine-containing hydrogel 2 was evaluated in a model of thermal nociception using the mouse tail-flick test. Sustained antinociceptive effects over extended periods of time (up to 24 h) for morphine co-formulated with hydrogel 2, compared to morphine injection in solution (effects up to 2 h), were observed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...