Phase II metabolic pathways of spectinamide antitubercular agents: a comparative study of the reactivity of 4-substituted pyridines to glutathione conjugation†
Abstract
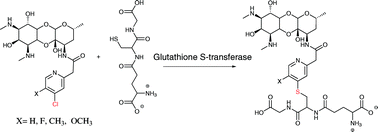
Spectinamides are promising new semisynthetic anti-tubercular agents that are modified with a pyridyl side chain, which blocks native efflux from the tuberculosis cell. This study, describes the stability of an advanced panel of spectinamide analogs, with varying substitutions to the pyridyl side chain, to Phase-II conjugative metabolism by glucuronosyl transferase, sulfotransferase and glutathione-S-transferase enzymes using both human and rat S9 enzyme fractions. All solely 5-substituted pyridyl spectinamides exhibited complete stability towards Phase II conjugative enzymes. However, 4-chloro substituted pyridyl spectinamides were susceptible to glutathione conjugation with rates dependent on other substitutions to the pyridine ring. Electron donating 5-substitutions increased the propensity for glutathione conjugation and conversely the introduction of an electron withdrawing 5-fluoro group blocked all observed glutathione conjugation. Based on these Phase II metabolism studies, lead spectinamides 1329, 1445, 1599, 1661 and 1810 were found to have favorable properties for potential lead compounds with no Phase II liabilities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...