Synthesis and biological evaluation of d-gluconhydroximo-1,5-lactam and its oxime-substituted derivatives as pharmacological chaperones for the treatment of Gaucher disease†‡
Abstract
D-Gluconhydroximo-1,5-lactam and its oxime-substituted derivatives were prepared and assessed for inhibition and pharmacological chaperone (PC) activities in Gaucher disease cell lines derived from N370S. The most active compound, O-(D-glucopyranosylidene) amino-Z-N-dodecylcarbamate (38), gave a nearly 2.0-fold increase in N370S β-GCase activity at 12.5 μM with no inhibition to other commercially available glucosidases. Docking studies of ligand–enzyme interactions have also been conducted to account for the results of enzyme activity increase. All these results demonstrate that compound 38 is a promising PC for the treatment of GD.
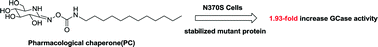

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...