Novel 1-(1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N,N-trimethylmethanaminium iodides are competitive antagonists for the human α4β2 and α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors†
Abstract
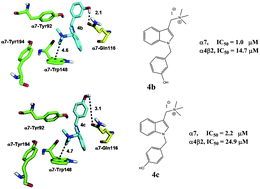
This work presents the synthesis and the pharmacological characterization of a series of novel 1-(1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl)-N,N,N-trimethylmethanaminium iodide derivatives at the human (h) α7 and α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The inhibitory activity of the compounds was determined by Ca2+ influx assays on cells expressing either the hα7 or hα4β2 nAChR subtype. To determine whether the observed inhibitory activity is mediated by a competitive or non-competitive mechanism, additional radioligand binding assays were performed using [3H]methyllycaconitine, [3H]cytisine, and [3H]imipramine. The results established that the compounds inhibit the nAChRs by a competitive mechanism and that the potencies are higher for the hα7 nAChR compared to that for the hα4β2 nAChR. Substitutions with oxygenated functional groups on the
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...