High-throughput malaria parasite separation using a viscoelastic fluid for ultrasensitive PCR detection†
Abstract
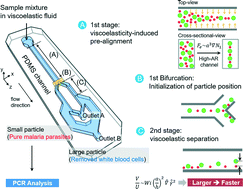
A novel microfluidic device for high-throughput particle separation using a viscoelastic fluid, which enables the rapid detection of extremely rare malaria parasites by using PCR analysis, is proposed. Our device consists of two segments: the 1st stage for sheathless pre-alignment and the 2nd stage for separation based on size-dependent viscoelasticity-induced lateral migration. The use of a high-aspect ratio channel and a viscoelastic polymer solution with low viscosity enables high-throughput processing. The device performance was first optimized using synthetic particles. A mixture of 2 and 10 μm particles was focused at the center plane in the 1st stage. The smaller particles, serving as surrogates for malaria parasites, were subsequently separated in the 2nd stage with a recovery rate of ∼96% at 400 μl min−1. Finally, separation of the malaria parasites from the white blood cells was performed. At 400 μl min−1, almost all white blood cells were removed and the malaria parasites were separated with a ∼94% recovery rate and ∼99% purity. Although the initial concentration of the malaria parasites was too low to be detected by PCR analysis, WBC depletion and buffer removal increased the parasite concentration sufficiently such that PCR detection was possible.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...