An optimised synthesis of high performance radiation-grafted anion-exchange membranes†
Abstract
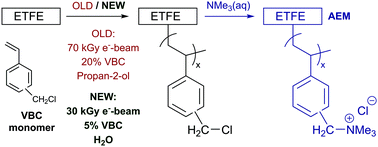
High performance benzyltrimethylammonium-type alkaline anion-exchange membranes (AEM), for application in electrochemical devices such as anion-exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFC), were prepared by the radiation grafting (RG) of vinylbenzyl chloride (VBC) onto 25 μm thick poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) films followed by amination with trimethylamine. Reductions in the electron-beam absorbed dose and amount of expensive, potentially hazardous VBC were achieved by using water as a diluent (reduced to 30–40 kGy absorbed dose and 5 vol% VBC) instead of the prior state-of-the-art method that used organic propan-2-ol diluent (required 70 kGy dose and 20 vol% VBC monomer). Furthermore, the water from the aqueous grafting mixture was easily separated from the residual monomer (after cooling) and was reused for a further grafting reaction: the resulting AEM exhibited an ion-exchange capacity of 2.1 mmol g−1 (cf. 2.1 mmol g−1 for the AEM made using a fresh grafting mixture). The lower irradiation doses resulted in mechanically stronger RG-AEMs compared to the reference RG-AEM synthesised using the prior state-of-the-art method. A further positive off-shoot of the optimisation process was the discovery that using water as a diluent resulted in an enhanced (i.e. more uniform) distribution of VBC grafts as proven by Raman microscopy and corroborated using EDX analysis: this led to enhancement in the Cl− anion-conductivities (up to 68 mS cm−1 at 80 °C for the optimised fully hydrated RG-AEMs vs. 48 mS cm−1 for the prior state-of-the-art RG-AEM reference). A down-selected RG-AEM with an ion-exchange capacity = 2.0 mmol g−1, that was synthesised using the new greener protocol with a 30 kGy electron-beam absorbed dose, led to an exceptional beginning-of-life H2/O2 AEMFC peak power density of 1.16 W cm−2 at 60 °C in a benchmark test using industrial standard Pt-based electrocatalysts and unpressurised gas supplies: this was higher than the 0.91 W cm−1 obtained with the reference RG-AEM (IEC = 1.8 mmol g−1) synthesised using the prior state-of-the-art protocol.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...