High molecular weight bio furan-based co-polyesters for food packaging applications: synthesis, characterization and solid-state polymerization†
Abstract
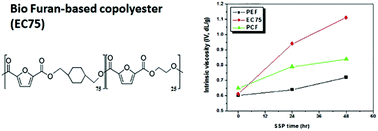
The goal of this study was to develop ecofriendly bioplastics, which could be applicable in beverage packaging, by synthesizing furan-based co-polyesters and incorporating them into bottles. The furan-based co-polyesters were synthesized by a two-step melt polycondensation reaction using ethylene glycol (EG), 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol (CHDM), and dimethyl furan dicarboxylate (DM-FDCA). The incorporation of CHDM into the main chain of polymers has been found to increase the chain mobility due to its ring-conformational transition, and it also affects the co-polyesters. The co-polyesters show not only high elongations at break, but also improved Izod impact strengths compared to that of pure poly(ethylene furanoate) (PEF). Despite these characteristics, however, the molecular weights of the co-polyesters were not sufficient for manufacturing purposes. Thus, some samples were further reacted in the solid state by solid state polymerization (SSP) to generate higher-molecular-weight polymers. The crystallization kinetics of the co-polyesters prepared were analyzed to determine the reaction parameters, and the sample whose intrinsic viscosity was greater than 1.0 dL g−1 was successfully processed into bottles. The bottles prepared had higher O2-barrier properties and lower acetaldehyde contents than those of commercially available PET bottles. The results obtained so far show that furan-based co-polyesters can be used for food-packaging applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...