Recovery of ibuprofen from pharmaceutical wastes using ionic liquids†
Abstract
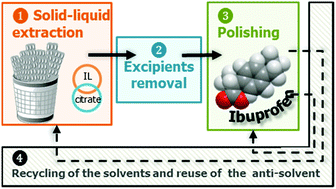
This work aims at developing a process to valorise pharmaceutical wastes through the recovery of pharmaceutically active compounds. The ibuprofen extraction and isolation from solid pharmaceutical wastes is used here as a case study and an integrated approach comprising the ibuprofen solid–liquid extraction, the removal of the insoluble excipients present in the pills, the target drug recovery and the recycling of the aqueous solutions is proposed. The present work is centred on the optimization of the first (solid–liquid extraction) and third (drug recovery) steps mentioned above. For the solid–liquid extraction step, various ionic liquid aqueous solutions were tested, tetrabutylammonium chloride ([N4444]Cl) being adopted to further optimize the process. A solution composed of 45 wt% of [N4444]Cl + 5 wt% of citrate buffer + 50 wt% of H2O led to the highest ibuprofen extraction efficiency (EEIBU = 97.92 ± 2.65%) while in the absence of citrate the extraction efficiency was somewhat lower (EEIBU = 93.53 ± 0.62%). The polishing task was affected by the type of aqueous solution utilized during the solid–liquid extraction step: in the presence of citrate buffer water was not prone to induce significant ibuprofen precipitation (maximum REIBU of 34.71 ± 4.00%) the aqueous KCl solution being the best option (maximum REIBU of 87.97 ± 1.00%); when no citrate buffer is used water can be used as an anti-solvent with a maximum REIBU of 91.60 ± 0.19% while aqueous KCl solutions lead to an REIBU up to 97.07 ± 0.14%. Based on these results an integrated process is proposed for the ibuprofen recovery and isolation aimed at adding value to pharmaceutical wastes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...