Enhancing the performance of Co-hydrothermal liquefaction for mixed algae strains by the Maillard reaction†
Abstract
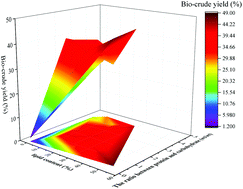
This study explored the effect of the Maillard reaction on the Co-Hydrothermal Liquefaction (HTL) of two different microalgae strains for bio-crude production. Model compounds, glucose and soya protein were mixed at different ratios and HTL was run at different temperatures to investigate the mechanism of the Maillard reaction. Pure Nannochloropsis (Nan), Spirulina (Spi) and the mixture of the two microalgae strains at the ratio of 1 : 1 (oven dry weight basis) were hydrothermally converted under the same reaction conditions for comparison. The mixtures of model compound and microalgae were also subjected to HTL to investigate the effects of chemical compounds on bio-crude yield. The Co-HTL for Nan and Spi exhibited lower bio-crude yield than that of HTL for individual microalgae. A high protein content has a negative effect on the fatty acid recovery. The dosage of glucose could enhance the bio-crude yield during HTL because of the Maillard reaction with protein. In addition, the results of elemental analysis indicated that the glucose dosage had promoted the energy recovery during HTL; FTIR and GC-MS spectra of bio-crudes revealing that tailoring the ratio between glucose and protein could elevate the quality of bio-crude from microalgae, especially for the microalgae with a low lipid content.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...