Highly selective transformation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone without using oxidants by a PtSb/C-catalyzed electrooxidation process†
Abstract
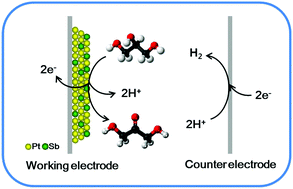
We demonstrate an electrocatalytic reactor system for the partial oxidation of glycerol in an acidic solution to produce value-added chemicals, such as dihydroxyacetone (DHA), glyceraldehyde (GAD), glyceric acid (GLA), and glycolic acid (GCA). Under optimized conditions, the carbon-supported bimetallic PtSb (PtSb/C) catalyst was identified as a highly active catalyst for the selective oxidation of glycerol in the electrocatalytic reactor. The product selectivity can be strongly controlled as a function of the applied electrode potential and the catalyst surface composition. The main product from the electrocatalytic oxidation of glycerol was DHA, with a yield of 61.4% of DHA at a glycerol conversion of 90.3%, which can be achieved even without using any oxidants over the PtSb/C catalyst at 0.797 V (vs. SHE, standard hydrogen electrode). The electrocatalytic oxidation of biomass-derived glycerol represents a promising method of chemical transformation to produce value-added molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...