Reductive amination of furfural to furfurylamine using aqueous ammonia solution and molecular hydrogen: an environmentally friendly approach†
Abstract
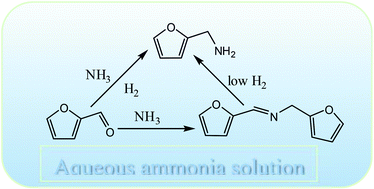
A simple and highly efficient method was developed for the transformation of furfural (a biomass derived aldehyde) to furfurylamine by reductive amination using an aqueous solution of ammonia and molecular hydrogen as an amine source and a reducing agent, respectively. By choosing a suitable catalyst, such as Rh/Al2O3, and reaction conditions, a very high selectivity of furfurylamine (∼92%) can be achieved within the reaction time of 2 h at 80 °C. A detailed analysis of the reaction system sheds some light on the reaction pathway and provides an understanding about each elementary step. The reaction was believed to proceed via an imine pathway although no such intermediate was detected because of the highly reactive nature. Optimization of different reaction parameters such as hydrogen pressure, temperature and substrate/ammonia mole ratio is shown to be critical to achieve high selectivity of furfurylamine. Time-dependent reaction profiles suggested that a Schiff base type intermediate was in the detectable range, which offers indirect evidence of the formation of imine. Competitive hydrogenation and amination of an aldehyde group were strongly dictated by the nature of the metal used. The studied protocol represents an environmentally benign process for amine synthesis, which can be effectively extended to the other aldehydes also. The studied catalyst could be recycled successfully without any significant loss of catalytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...