2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside exerted protective effects on diabetic nephropathy in mice with hyperglycemia induced by streptozotocin
Abstract
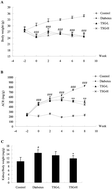
2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside (TSG), an active component from the functional and medicinal herb Polygonum multiflorum Thunb, has the capacity of blocking angiotensin II (ANG II) signaling, a pathway within the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) which plays a critical role in the development of diabetic nephropathy (DN), and blockade of the RAS is currently used for the treatment of DN. Here we investigated the beneficial effect of TSG therapy on renal damage in the streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes model. The STZ-treated C57BL/6J diabetic mice developed progressive albuminuria and renal tubular interstitial fibrosis within 10 weeks, accompanied by increased production of ANG II, fibronection, TGF-β, CTGF, TNF-α, RANTES and MCP-1 and decreased expression of slit diaphragm proteins in the kidney. The treatment of the diabetic mice with a TSG ameliorated kidney mass increase prevented albuminuria, and reduced tubular interstitial fibrosis. The TSG treatment suppressed the induction of fibronection, CTGF, TGF-β, and MCP-1 and reversed the decline of slit diaphragm proteins Neph-1, ZO-1, and FAT-1. These were accompanied by blockade of renal renin and ANG II accumulation induced by hyperglycemia. These data demonstrated that the inhibition of the RAS with TSG effectively prevented renal injury in diabetic nephropathy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...