Compound K derived from ginseng: neuroprotection and cognitive improvement
Abstract
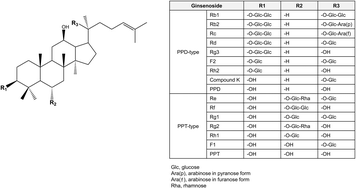
The evidence for the neuroprotective and cognitive effects of compound K, a metabolite biotransformed from ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, and Rc, is reviewed here. Compound K is more bioavailable than other ginsenosides and therefore has greater potential to exert bioactive functions in the body. Although the capability of compound K to cross the blood–brain barrier is not clear, it has been reported to have neuroprotective and cognition enhancing effects and decrease inflammatory biomarkers in animal models of Alzheimer's disease and cerebral ischemia. The plethora of potential health benefits of compound K warrants further research to evaluate its biochemical mechanisms and its ability to protect healthy populations from neurodegenerative diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...