Laminarin favorably modulates gut microbiota in mice fed a high-fat diet†
Abstract
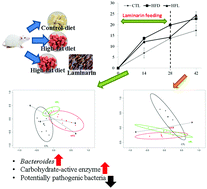
We investigated the anti-obesity effects of the potential prebiotic, laminarin, on mice fed a high-fat diet. A metagenomics approach was applied to characterize the ecological and functional differences of gut microbiota among mice fed a normal diet (CTL), a high-fat diet (HFD), and a laminarin-supplemented high-fat diet (HFL). The HFL mice showed a slower weight gain than the HFD mice during the laminarin-feeding period, but the rate of weight gain increased after the termination of laminarin supplementation. Gut microbial community analysis showed clear differences between the CTL and HFD mice, whereas the HFL mice were between the two. A higher abundance of carbohydrate active enzymes was observed in the HFL mice compared to the HFD mice, with especially notable increases in glycoside hydrolase and polysaccharide lyases. A significant decrease in Firmicutes and an increase in the Bacteroidetes phylum, especially the genus Bacteroides, were observed during laminarin ingestion. Laminarin ingestion altered the gut microbiota at the species level, which was re-shifted after termination of laminarin ingestion. Therefore, supplementing laminarin could reduce the adverse effects of a high-fat diet by shifting the gut microbiota towards a higher energy metabolism. Thus, laminarin could be used to develop anti-obesity functional foods. Our results also suggest that laminarin would need to be consumed regularly in order to prevent or manage obesity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...