Piceatannol is superior to resveratrol in promoting neural stem cell differentiation into astrocytes
Abstract
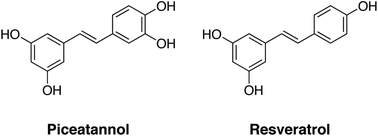
Piceatannol (3,3′,4′,5-trans-tetrahydroxystilbene) is a polyphenolic compound abundant in the seeds of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis). Piceatannol is an analogue of resveratrol (3,4′,5-trans-trihydroxystilbene) and shares the structural motif and biological activities such as activation of SIRT1. Several studies have shown that piceatannol is more potent than resveratrol. In this study, we examined the effects of piceatannol on neural stem cell differentiation into astrocytes compared with those of resveratrol. At a concentration of 2.5 μM, piceatannol promoted astrocyte differentiation, while resveratrol had no effect at this concentration. Furthermore, we found that oral administration of piceatannol increased the number of astrocytes in the brains of adult mice, while resveratrol administration showed no effects. These results suggest that piceatannol has a superior effect to resveratrol in promoting astrocyte differentiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...