Efficacy of nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, in the treatment of the cardiovascular dysfunction of diabetes in rats
Abstract
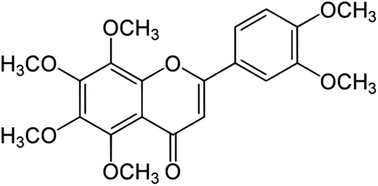
Hyperglycemia induced oxidative stress is a prime factor for cardiovascular dysfunction (CVD) in diabetic patients. In this process matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) play important roles. Nobiletin, a polymethoxy citrus flavone, has potent MMP-2 and MMP-9 inhibitory activity in addition to antioxidant activity. We hypothesized that nobiletin due to its MMP-2 & MMP-9 inhibitory and antioxidant effects may ameliorate the cardiovascular dysfunction of diabetes. Diabetes was induced using streptozotocin (50 mg kg−1 i.p.) in male wistar rats. Four weeks after the induction of diabetes, the rats were treated with nobiletin (10 mg kg−1, and 25 mg kg−1) for a period of the following four weeks. At the end of eight weeks, hemodynamic parameters were recorded, cardiac hypertrophy was measured, and antioxidant assays, and gelatin zymography for MMP-2 & MMP-9 analysis and histopathology were performed. The vascular reactivity of the aorta was measured by recording the contractile response to phenylephrine and relaxation responses to acetylcholine. Treatment with 25 mg kg−1 nobiletin ameliorated the hemodynamic parameters, oxidative stress, collagen level, MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels, and vascular reactivity significantly compared with vehicle treated diabetic group. Thus, this study suggests that nobiletin ameliorates the CVD of diabetes by inhibiting oxidative stress, MMP-2 & MMP-9 and can be used as a potential therapeutic approach.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...