Protective effects of Chaenomeles thibetica extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced damage via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
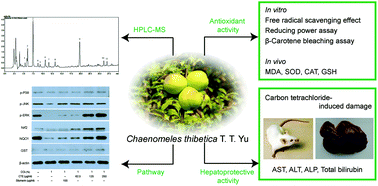
Chaenomeles thibetica, a type of fruit of the genus Chaenomeles, is commonly cultivated and used as Mugua in China and as liquor, candy, and functional food in Tibet. Total phenol, flavonoid, and proanthocyanidin contents were measured in C. thibetica extract (CTE). CTE had a positive effect on free radical scavenging and anti-lipid oxidation in vitro. The protective effects of CTE against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced oxidative damage in vivo were also measured. The results of antioxidative enzymes indicated that CTE can increase the activities of the catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione contents and reduce the level of malondialdehyde in rats. The levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate transaminase, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin were significantly reversed by CTE compared with the elevated levels in the CCl4 group. Besides, CTE could reverse the cell viability of HepG2 inoculated with CCl4via phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), activating the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2) and increasing the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes. These effects may expand the applications of C. thibetica and offer alternative food with antioxidant and hepatoprotective functions in the food industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...