Protective effects of ginsenoside Re on lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction in mice
Abstract
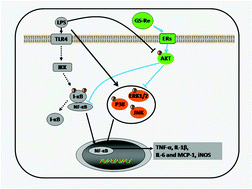
The impaired cardiac function caused by reduced myocardial contractility is a typical manifestation of sepsis/septic shock. Ginsenoside Re (GS-Re) is one of the most abundant ingredients of ginseng. This study was designed to investigate the protective effects of GS-Re on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced septic cardiac dysfunction and inflammatory response in mice. Mice were intragastrically administered with GS-Re (15 mg kg−1) for 1 week before the LPS challenge (10 mg kg−1, i.p.). Cardiac function was evaluated 6 h after LPS induction. GS-Re pretreatment significantly protected against LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction. GS-Re ameliorated the imbalance between iNOS and eNOS, and prevented NF-κB activation and subsequent myocardial inflammatory responses in endotoxemic mice. The effects of GS-Re were closely associated with estrogen receptors (ERs), phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling, and the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway, as characterized by the GS-Re-induced preservation of ERα, ERβ, and phospho-Akt and inhibition of phospho-ERK1/2, phospho-JNK, phospho-P38. However, GS-Re had no effect on LPS-induced activation of TLR-4. All these results showed that GS-Re pretreatment significantly attenuated LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction and inflammatory response.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...