Enhancement of carotenoid bioaccessibility from carrots using excipient emulsions: influence of particle size of digestible lipid droplets
Abstract
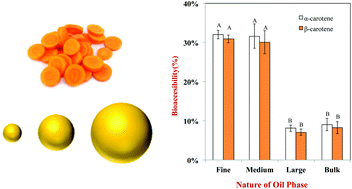
The influence of initial lipid droplet size on the ability of excipient emulsions to increase carotenoid bioaccessibility from carrots was investigated using a simulated gastrointestinal tract (GIT). Corn oil-in-water excipient emulsions were fabricated with different surface-weighted mean droplet diameters: d32 = 0.17 μm (fine), 0.46 μm (medium), and, 10 μm (large). Bulk oil containing a similar quantity of lipids as the emulsions was used as a control. The excipient emulsions and control were mixed with pureed carrots, and then passed through a simulated GIT (mouth, stomach, and small intestine), and changes in particle size, charge, microstructure, lipid digestion, and carotenoid bioaccessibility were measured. Carotenoid bioaccessibility significantly increased with decreasing lipid droplet size in the excipient emulsions, which was attributed to the rapid formation of mixed micelles that could solubilize the carotenoids in the intestinal fluids. These results have important implications for designing excipient foods, such as dressings, dips, creams, and sauces, to increase the bioavailability of health-promoting nutraceuticals in foods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...