Rapid prototyping of electrolyzer flow field plates†
Abstract
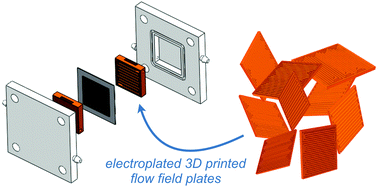
Electrolyzers use electricity to convert water into hydrogen fuels that can be stored for prolonged time periods. The large-scale deployment of electrolyzers for energy storage is hampered by catalyst efficiencies as well as high capital costs. Herein we report a rapid prototyping methodology to accelerate the development of complex flow plate architectures as a means of lowering electrolyzer capital costs. This process involves the electroplating of nickel onto 3D-printed plastic flow cells, which enable the rapid production of experimental flow plates with different flow channel geometries. The test cells containing these metal-coated plastic components matched the performance of conventional metal electrodes. The ability to electroplate 3D-printed parts offers the opportunity to rapidly prototype flow-field geometries to more rapidly evaluate fluid and gas flow through the electrolyzer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...