CO2 enabled process integration for the production of cellulosic ethanol using bionic liquids†
Abstract
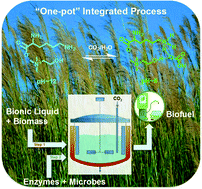
There is a clear and unmet need for a robust and affordable biomass conversion technology that can process a wide range of biomass feedstocks and produce high yields of fermentable sugars and biofuels with minimal intervention between unit operations. The lower microbial toxicity of recently-developed renewable ionic liquids (ILs), or bionic liquids (BILs), helps overcome the challenges associated with the integration of pretreatment with enzymatic saccharification and microbial fermentation. However, the most effective BILs known to date for biomass pretreatment form extremely basic pH solutions in the presence of water, and therefore require neutralization before the pH range is acceptable for the enzymes and microbes used to complete the biomass conversion process. Neutralization using acids creates unwanted secondary effects that are problematic for efficient and cost-effective biorefinery operations using either continuous or batch modes. We demonstrate a novel approach that addresses these challenges through the use of gaseous carbon dioxide to reversibly control the pH mismatch. This approach enables the realization of an integrated biomass conversion process that eliminates the need for intermediate washing and/or separation steps. A preliminary technoeconomic analysis indicates that this integrated approach could reduce production costs by 50–65% compared to previous IL biomass conversion methods studied.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...