Single layer graphene encapsulating non-precious metals as high-performance electrocatalysts for water oxidation†
Abstract
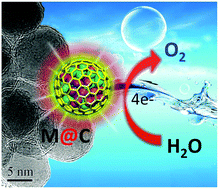
The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is recognized as a key half-reaction in water electrolysis for clean hydrogen energy, which is kinetically not favored and usually requires precious metal catalysts such as IrO2 and RuO2 to reduce the overpotential. The major challenge in using non-precious metals in place of these precious metal catalysts for OER is their low efficiency and poor stability, which urgently demand new concepts and strategies to tackle this issue. Herein, we report a universal strategy to directly synthesize single layer graphene encapsulating uniform earth-abundant 3d transition-metal nanoparticles such as Fe, Co, Ni and their alloys in a confined channel of mesoporous silica. The single atomic thickness of the graphene shell immensely promotes the electron transfer from the encapsulated metals to the graphene surface, which efficiently optimizes the electronic structure of the graphene surface and thereby triggers the OER activity of the inert graphene surface. We investigated a series of non-precious 3d metals encapsulated within single layer graphene, and found that the encapsulated FeNi alloy showed the best OER activity in alkaline solutions with only 280 mV overpotential at 10 mA cm−2, and also possessed a high durability after 10 000 cycles. Both the activity and durability of the non-precious catalyst even exceed that of the commercial IrO2 catalyst, showing great potential to replace precious metal catalysts in the OER.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...