Molecular-ink route to 13.0% efficient low-bandgap CuIn(S,Se)2 and 14.7% efficient Cu(In,Ga)(S,Se)2 solar cells†
Abstract
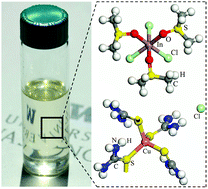
A stable dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)-based ink containing a copper–thiourea–chloride complex and an indium–DMSO–chloride complex leads to 13.0% efficient CuIn(S,Se)2 (CIS) solar cells, which is a record for solution processed CIS. The formation of these complexes was found critical to control oxidation states and loss of metals during processing and to tailor the final composition of the absorber.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...