Water assisted high proton conductance in a highly thermally stable and superior water-stable open-framework cobalt phosphate†
Abstract
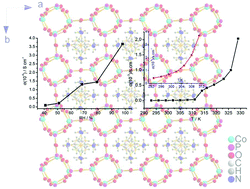
Proton-conducting materials show important technological applications as key components in energy conversion, electrochemical sensing and electrochromic devices; the exploration for new types of proton-conducting materials is crucial for the development of efficient electrochemical devices. In this study, we investigated the proton transport nature of an inorganic–organic hybrid crystal of open-framework cobalt phosphate, (C2N2H10)0.5CoPO4. The structure of the hybrid crystal consists of the [CoPO4]−∞ anionic framework, and the proton carriers, H2en2+ cations (en = ethylenediamine), are located in the pores to compensate the negative charges of the inorganic framework. The open-framework is thermally stable up to 653 K (380 °C) at least, and also shows superior water stability. The open-framework exhibits negligible conductance in an anhydrous environment even at 473 K; however, there is evident water-assisted proton conduction. The conductivity reaches 2.05 × 10−3 S cm−1 at 329 K and 98% RH. Such high proton conductivity can compete with numerous state-of-the-art MOFs/PCPs-based proton conductors, and this material has promising applications in diverse electrochemical devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...