Reduction of a tris(picolyl)amine copper(ii) complex by a polymeric flavo-reductase model in water†
Abstract
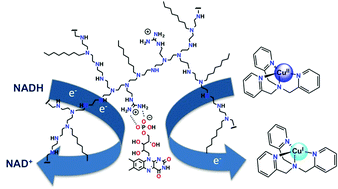
Dioxygen activation at copper(I) centres is of primary importance for the development of sustainable oxidation catalysis, but regeneration of copper(I) centres after each catalytic cycle remains a major problem for multi-turn-over catalysis. This work demonstrates that an artificial reductase, made of flavin cofactors incorporated into a water soluble polymer, efficiently reduces a Cu(II)TPA complex in the presence of NADH in water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...